Remote Device Control
The coScene platform enables real-time remote device operations, such as remote command execution and SSH connections, enhancing operational capabilities.
Prerequisites
- The device has coScene client programs installed. For details, please refer to Device Installation.
- The organization administrator has granted device access and permitted remote control operations. For details, please refer to Enable Device.
- The device has been added to the project. For details, see Assign Devices to Projects.
Real-time Visualization
Prerequisites:
Ensure that the coBridge component is installed and running on the device.
coBridge is an independent ROS node responsible for real-time transmission of device data to the frontend via the WebSocket protocol.
It is part of the ROS suite. If the ROS node has already been installed and enabled, coBridge does not need to be installed again.
- See coBridge Installation Guide
- Run and start:
# for ROS 1 distribution
roslaunch cobridge cobridge.launch
# for ROS 2 distribution
ros2 launch cobridge cobridge_launch.xml
It is strongly recommended to compile coBridge from source (Build Guide), integrate it into your robot software, and add the startup command to the robot’s startup script.
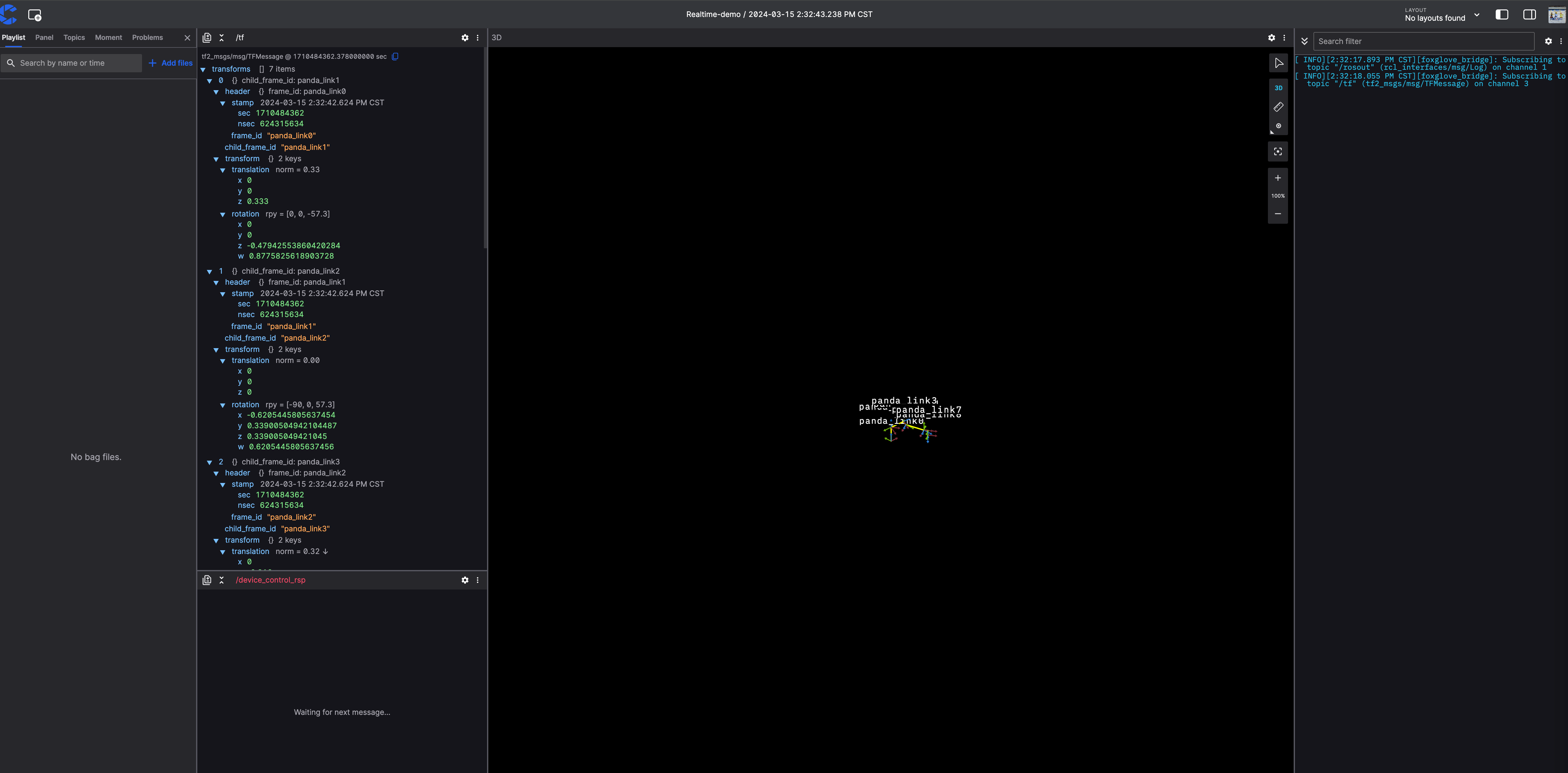
Once the coBridge node is running, with a public address and port mapped via virmesh, you can subscribe to robot topics, call services, and perform other operations through the web interface to achieve real-time remote visualization of the robot.
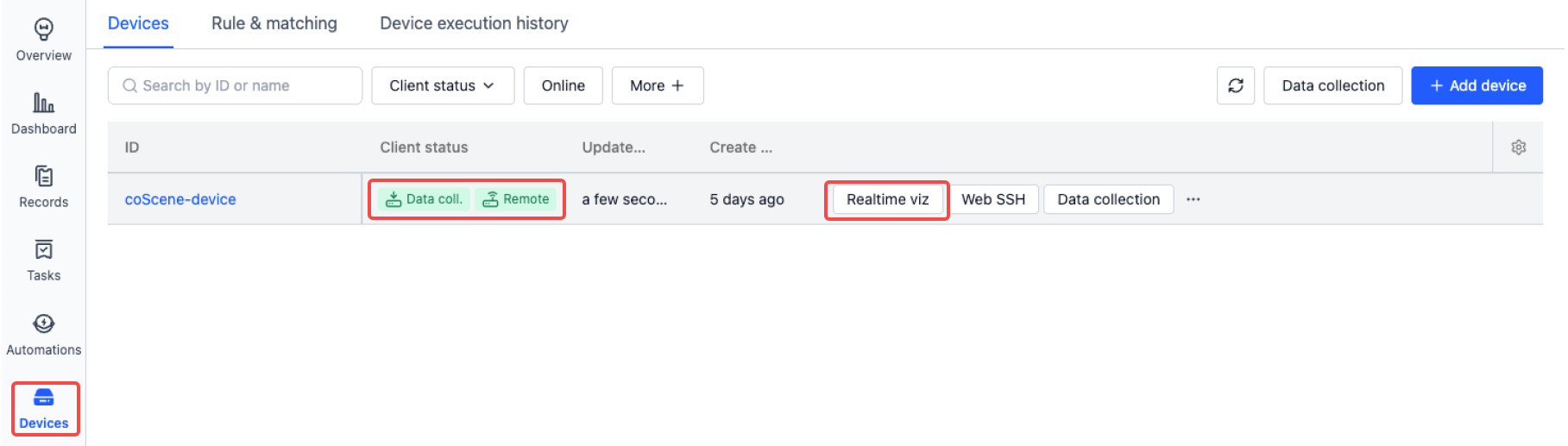
On the Project - Devices page, when the client status is Online, a Realtime Viz button will appear next to the device.
Click the button to view the live status of the machine.
Web SSH
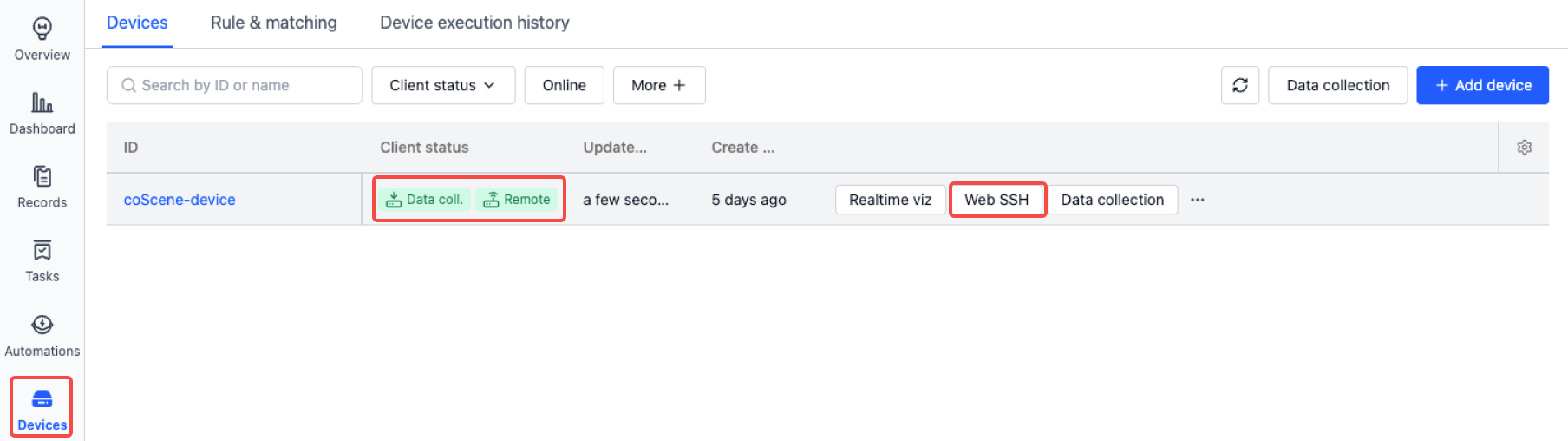
On the Project - Devices page, when the client status is Online, a Web SSH button will appear, which opens a new browser tab to establish an SSH connection to the device.
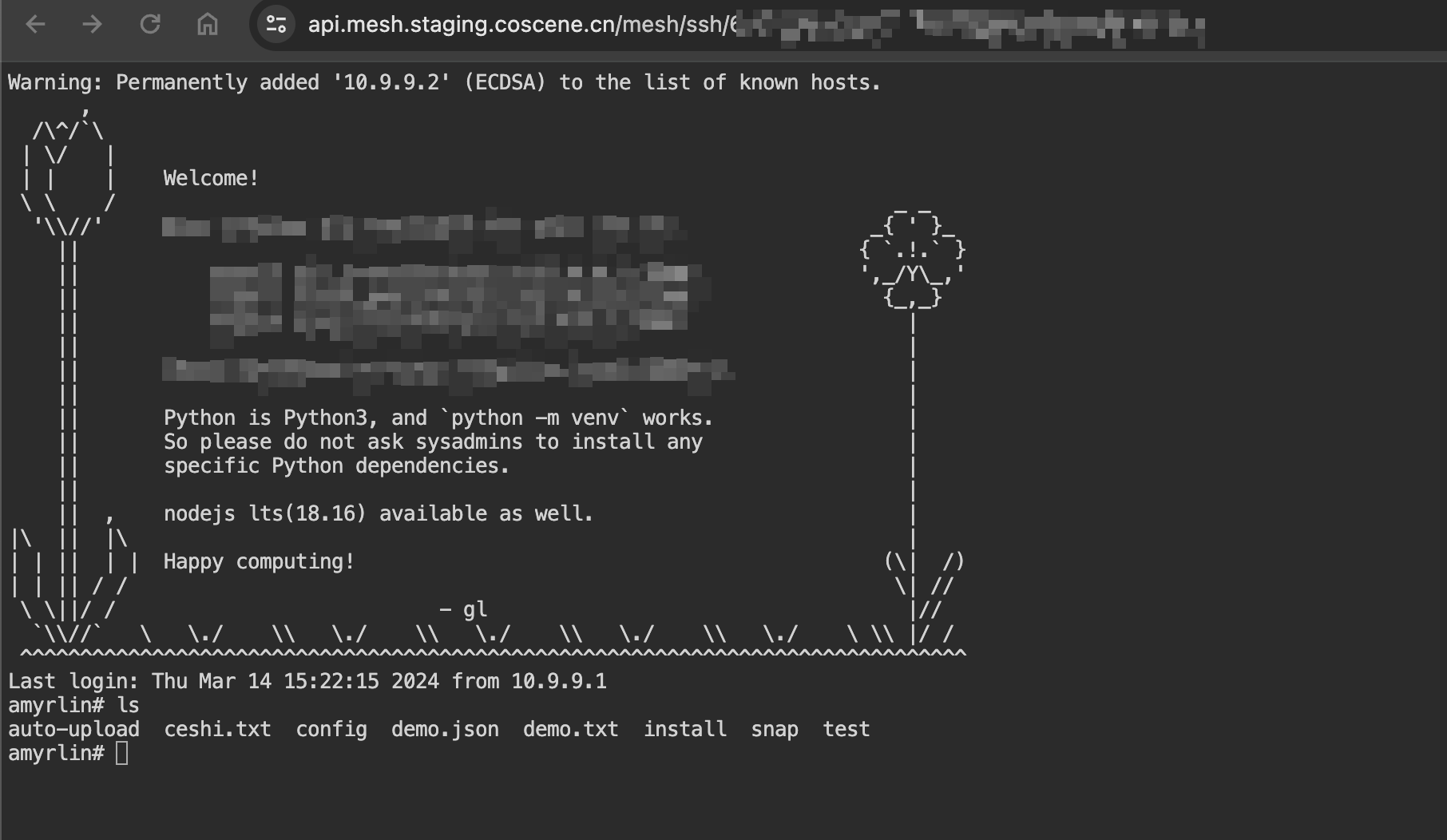
The page comes with Trzsz file transfer tool by default. Users can upload local files to the remote device using the trz file1 command, and download files from the remote device using tsz file1 file2 file3. For more advanced usage, please refer to the detailed documentation.
Remote Command
When a device is online remotely, users can execute specific tasks by sending commands through the Remote Command feature. You can also perform batch operations on multiple devices simultaneously.
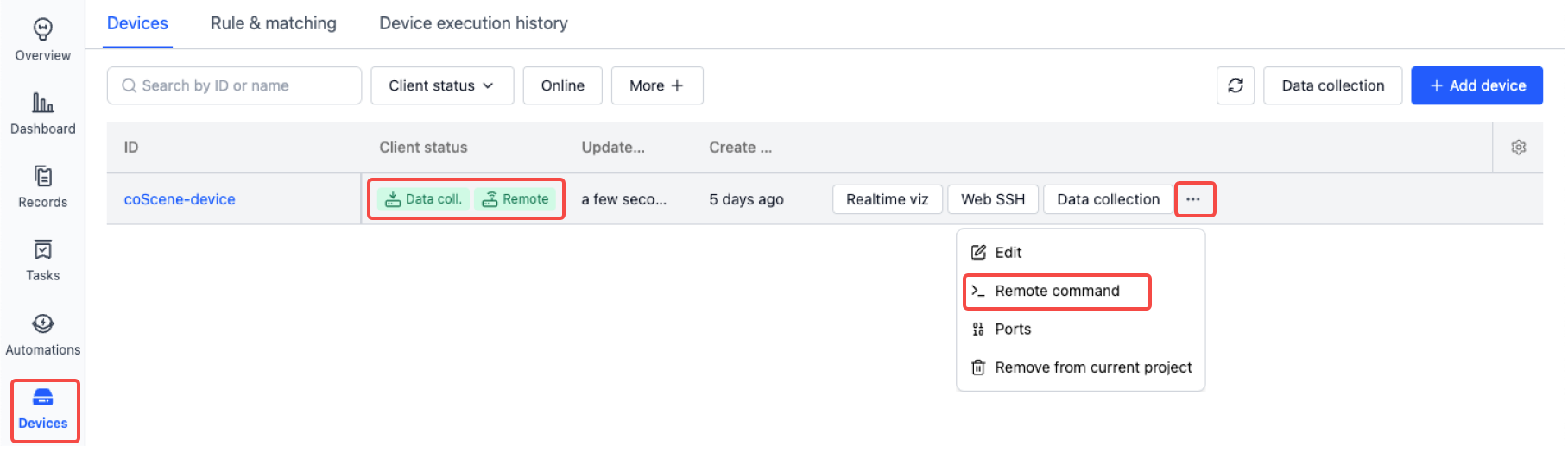
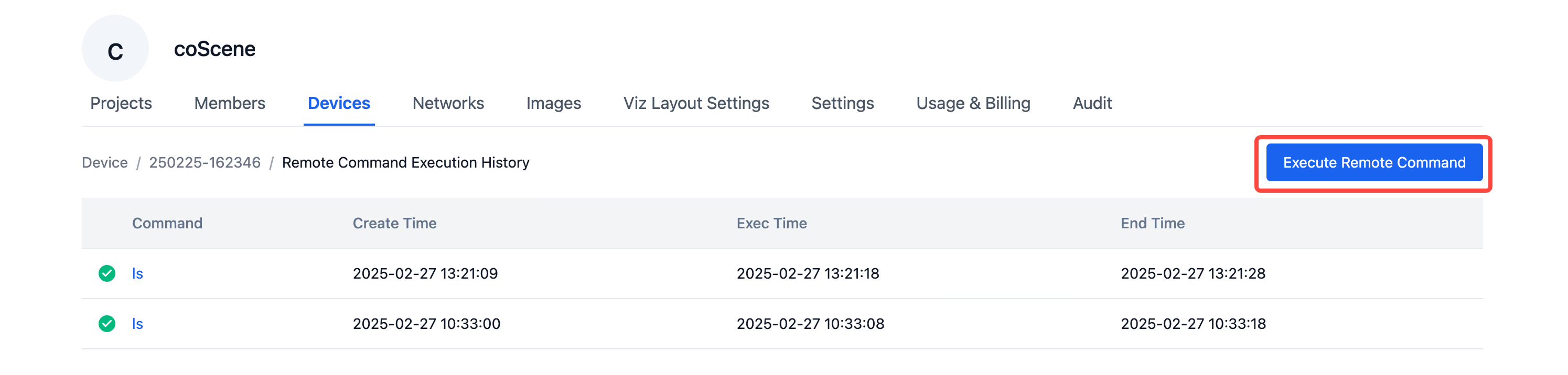
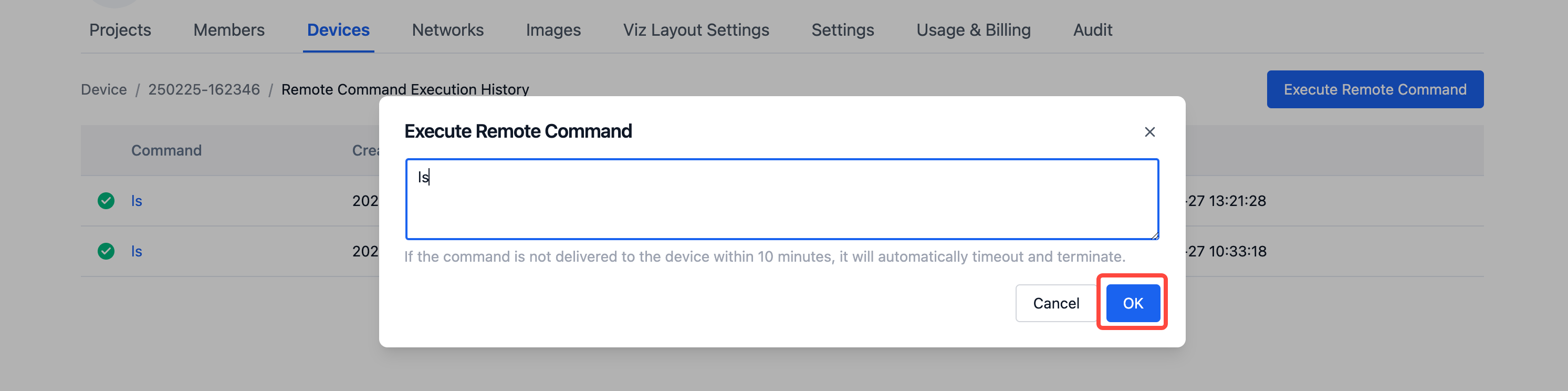
Click the [Execute Remote Command] button, enter the command you want to execute in the popup window, and click the [OK] button to execute the command on the device.
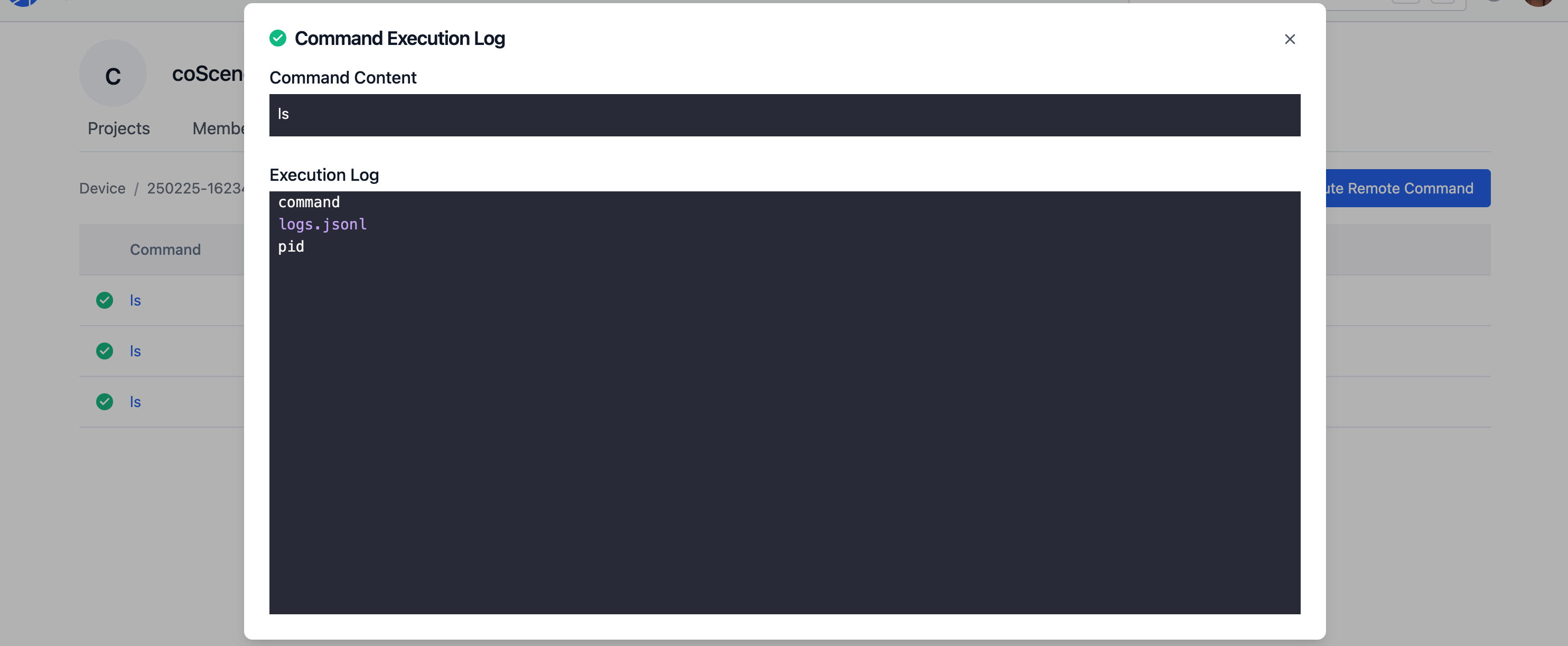
After the command executes successfully, you can view the log results.
Port Forwarding
When a device doesn't have a public IP, users cannot directly access its ports. The port forwarding feature allows device ports to be forwarded, making them accessible over the public network. This is useful for temporarily exposing device services or debugging local connections.
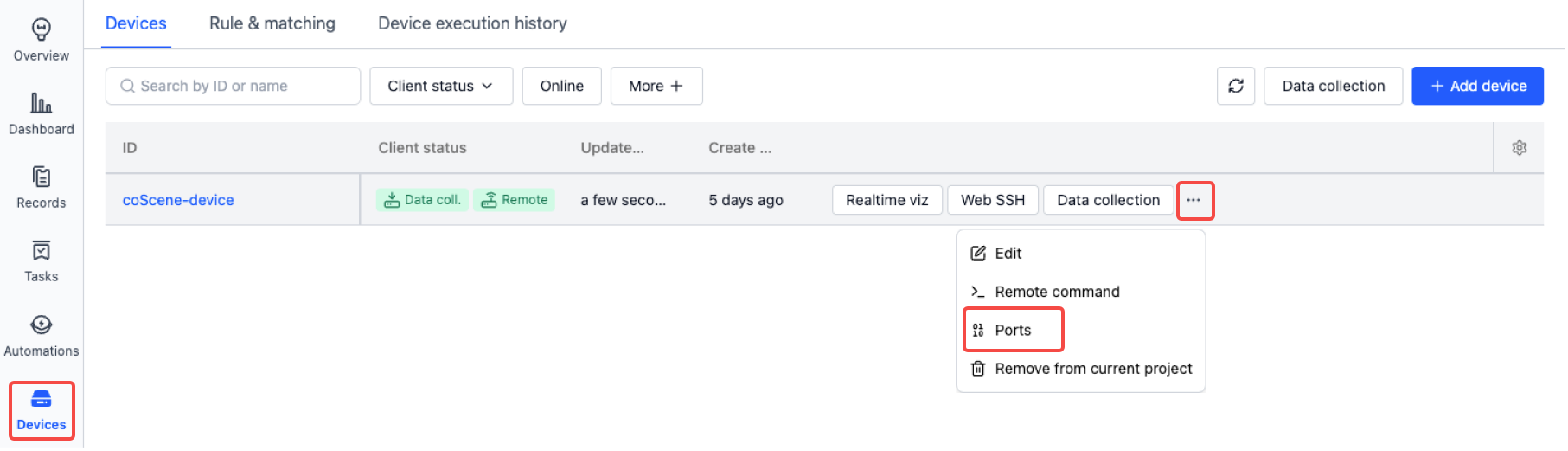
Here's a simple example. Using the [Web SSH] feature, we connect to the remote device and run python3 -m http.server 9000 -d ~ to start a simple HTTP Server that serves files from the ~ directory. The server listens on port 9000, which we then configure for forwarding. After this, we can access the forwarded address from our local browser to reach the device.
-
Configure port 9000 forwarding in the web interface
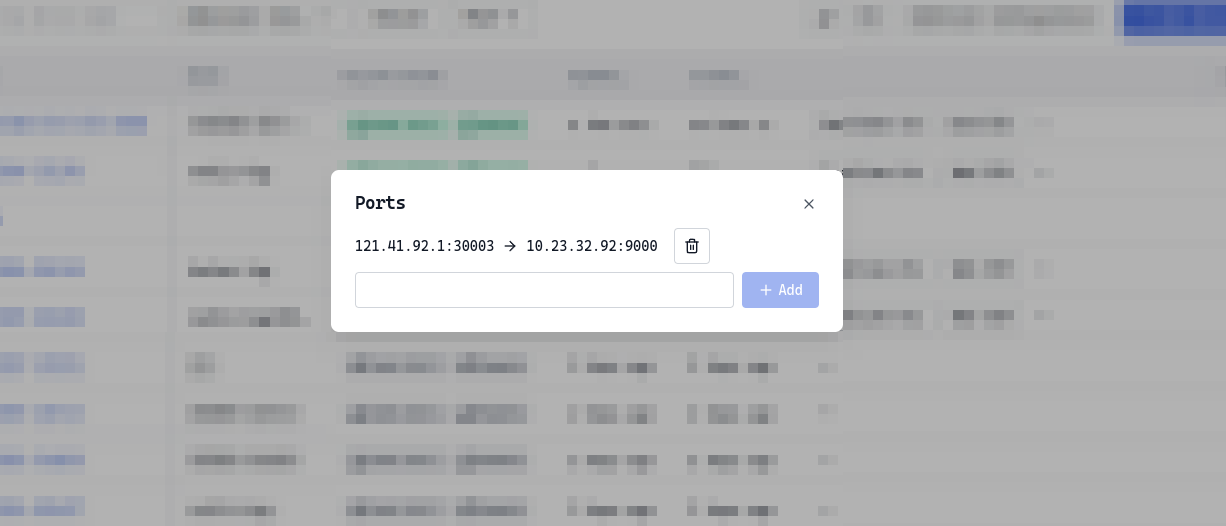
-
Start a simple HTTP Server using Web SSH by executing
python3 -m http.server 9000 -d ~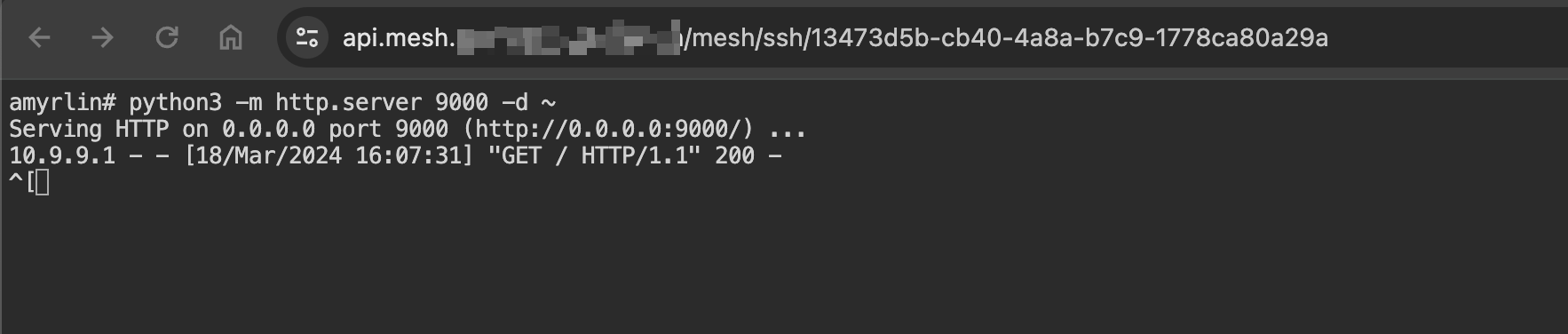
-
Access the forwarded address in the browser to see all files in the device's
~directory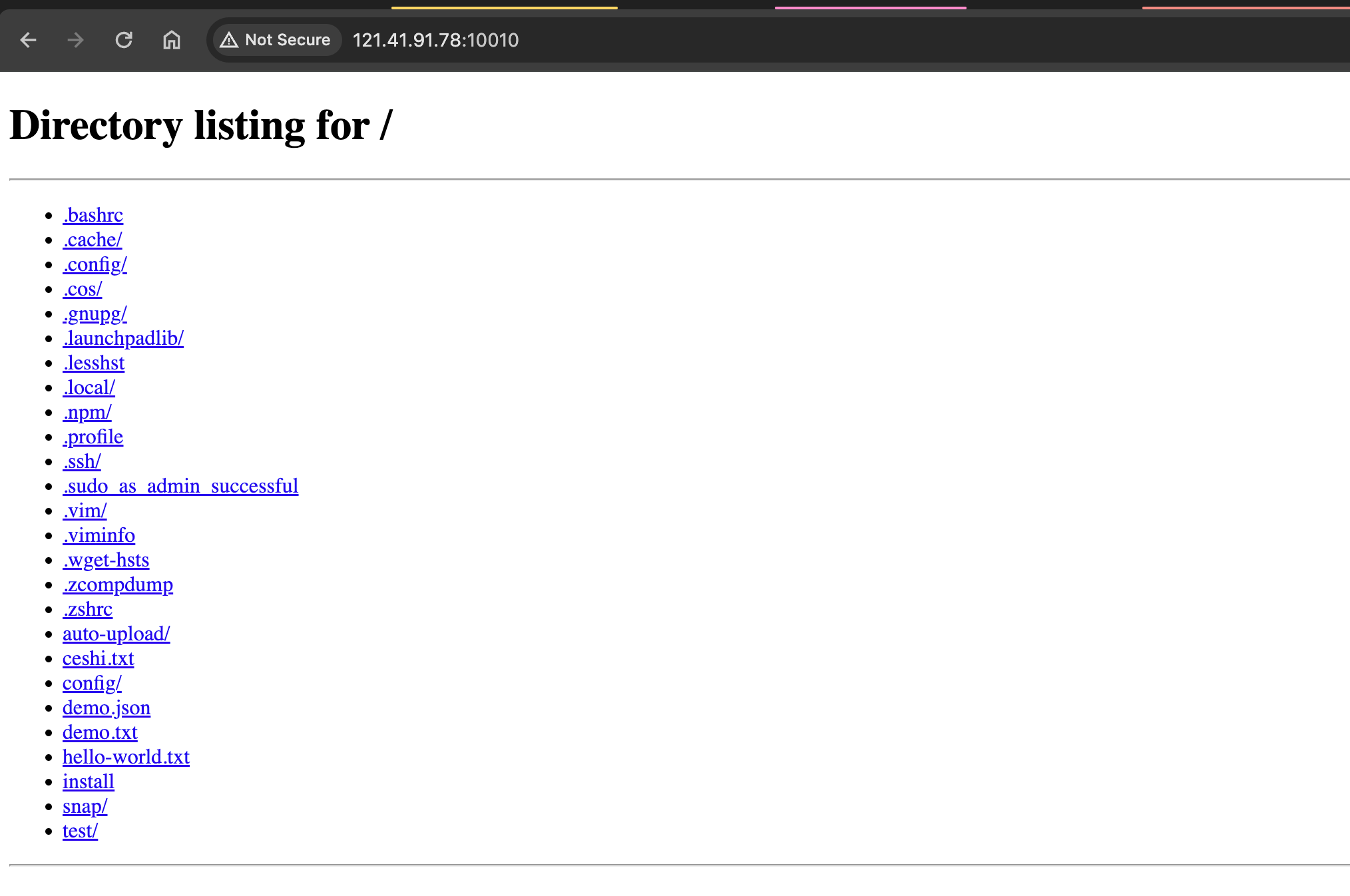
-
Check the device logs to confirm that browser requests are being forwarded and returning 200 status codes
